|
|
Previous | 1 | Next
| ANTHONE >> Recorders |
| Anthone Paperless Recorders Selection Guide |
|
|
Picture |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Model: |
LC-2100 (Blue) |
LU-C500 Active Color LCD |
LU-R5000 TFT LCD |
LU-C1000 PID |
LU-R1000 |
LU-R3000 Color |
|
Supply |
85VAC!264VAC, 50 Hz+/- 1 Hz, 12 W
|
85VAC!264VAC, 50 Hz+/- 1 Hz, 12 W |
85VAC!264VAC, 50 Hz+/- 1 Hz, 12 W |
85VAC!264VAC, 50 Hz+/- 1 Hz, 12 W |
85VAC!264VAC, 50 Hz+/- 1 Hz, 12 W |
85VAC!264VAC, 50 Hz+/- 1 Hz, 12 W |
|
Display |
320×240 high resolution chart blue-white LCD |
10.4 inch TFT active color LCD, resolution 640×480, high light , none view angle. |
10.4 inch TFT active color LCD, resolution 640×480, high light , none view angle. |
|
|
320×240 high resolution chart blue-white LCD |
|
Inputs |
Standard voltage 0-5V, 1-5V
standard current 0-10mA, 4-20mA
T.C: K, S, B, T, E, J, Wre325, N
RTD: Pt100, Cu50, Cu100
specially input: R, WRe526, mV signal, other |
Standard voltage 0-5V, 1-5V
standard current 0-10mA, 4-20mA
T.C: K, S, B, T, E, J, Wre325, N
RTD: Pt100, Cu50
Special input: R, Wre526, mV signal, other |
Standard voltage 0-5V, 1-5V
standard current 0-10mA, 4-20mA
T.C: K, S, B, T, E, J, Wre325, N RTD: Pt100, Cu50
Special input: R, Wre526, mV signal, other |
standard voltage 0-5V, 1-5V
standard current 0-10mA, 4-20mA
T.C: K, S, B, T, E, J, Wre325, N
RTD: Pt100, Cu50, Cu100
specially input: R, WRe526, the mV signal, other (indicated when ordering) |
standard voltage 0-5V, 1-5V
standard current 0-10mA, 4-20mA
T.C: K, S, B, T, E, J, Wre325, N
RTD: Pt100, Cu50, Cu100
specially input: R, WRe526, the mV signal, other (indicated when ordering) |
Standard voltage 0-5V, 1-5V;
standard current 0-10mA, 4-20mA
T.C: K, S, B, T, E, J, Wre325, N
RTD: Pt100, Cu50, Cu100
specially input: R, WRe526, the mV signal, other |
|
Outputs |
Switch output: Relay contact output (resistance 250VAC/0.8A or 250VAC/3A)
linear current output: 0-10mA, 4-20mA, 0-20mA (software free set)
linear voltage output: 0-5V, 1-5V, 0-10V (indicates when ordering)
silicon-controlled zero-crossing trigger the SSR trigger (12V/50mA) DC12V/50mA DC24V/50mA DC5V/50mA
the transform output: 4-20mA (the load <650Ω)、1-5V 0-10mA(the load <1000Ω)、0-5V
Communication connection: RS232 or RS485 storage medium: U disk/256M, U disk/512M |
Switch output: Relay contact output (resistance 250VAC/0.8A or 250VAC/3A)
linear current output: 0-10mA, 4-20mA, 0-20mA (software free set)
linear voltage output: 0-5V, 1-5V, 0-10V (indicates when ordering)
silicon-controlled zero-crossing trigger the SSR trigger (12V/50mA) DC12V/50mA DC24V/50mA DC5V/50mA transform output: 4-20mA (the load <650Ω)、1-5V 0-10mA(the load <1000Ω)、0-5V
Communication connection: RS232 or RS485 storage medium: U disk/256M, U disk/512M |
Switch output: Relay contact output (resistance 250VAC/0.8A or 250VAC/3A) the SSR trigger (12V/50mA) DC12V/50mA DC24V/50mA DC5V/50mA transform output: 4-20mA (the load <650Ω)、1-5V 0-10mA(the load <1000Ω)、0-5V
Communication connection: RS232 or RS485 storage medium: U disk/256M, U disk/512M |
Switch output: Relay (resistance 250VAC/0.8A or 250VAC/3A)
Linear current output: 0-10mA, 4-20mA, 0-20mA (software sets freely)
Linear voltage output: 0-5V, 1-5V, 0-10V (indicated when ordering)
Silicon-controlled zero-crossing trigger;SSR trigger (12V/50mA)
Sensor power supply: DC12V/50mA DC24V/50mA; DC5V/50mA
transform output: 4-20mA (load <650Ω), 1-5V ; 0-10mA (load <1000Ω), 0-5V
communication connection: RS232 or RS485
storage medium: U disk/512M, U disk/1G, U disk/2G |
|
|
|
USB Storage |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Options |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| BM Technologies >> Radar |
| Pulse Radar Selection Guide |
BM Tech Radar Level Transmitter Selection Guide
|
Picture |
Model No. |
Application |
Frequency |
Power |
Op.Temp. |
Range |
Accuracy |
Resolution |
Antenna |
Process Connection
|
Output |
 |
CW51 |
Liquids |
6.3 Ghz |
24 VDC
230VAC
|
-40 ~120oC |
20 M |
10mm |
1mm |
Rod
PP/ PTFE
|
G1-1/2" A NPT |
2/4 wires
4~20mA;
Hart Protocol
|
 |
CW52 |
Liquids |
6.3 Ghz |
24 VDC
230VAC
|
-40 ~150oC
|
30 M |
10 mm |
1 mm |
Rod
PP/PTFE
|
SS316L PN16, DN50,100,150,
200,250,300PTFE
|
2/4 wires 4-20mA;
Hart Protocol
|
 |
CW53 |
Liquids
Solids
|
6.3 Ghz |
24 VDC
230VAC
|
-40 ~200oC |
30 M |
10 mm |
1 mm |
Conicals Dia. 50,80,100,
150,200mm
|
SS316L PN16, DN50,100,150,
200,250,300 PTFE
|
2/4Wires
4-20mA;
Hart Protocol
|
 |
CW54 |
Liquids |
6.3 Ghz |
24 VDC
230VAC
|
-40
~200oC
|
70 M |
20 mm |
1 mm |
Conicals
Dia 150,200mm
SS316L
|
Flanges
SS316L
PN 16 DN150,200
|
2/4 wires 4-20mA;
Hart Protocol
|
 |
CW55 |
Liquids |
26 Ghz |
24 VDC
230VAC
|
-40
~130oC
|
10 M |
5 mm |
1 mm |
Pole
PVDF
PTFE
|
G1-1/2" A-NPT |
2/4 wires 4-20mA;
Hart Protocol
|
 |
CW56 |
Liquids
Solids
|
26 Ghz |
24 VDC
230VAC
|
-40
~400oC
|
30 M |
3 mm |
1 mm |
Cones Dia 48,78,98,123 |
G1-1/2" A
Flange DN50,90,100
150, AISI 316L
|
2/4 wires 4-20mA;
Hart Protocol
|
 |
CW57 |
Liquids
Solids
|
26 Ghz |
24 VDC
230VAC
|
-40
~150oC
|
20 M |
3 mm |
1 mm |
Conical Dia
40,48,75,95
PTFE
|
Flanges
DB50,80,100
150 AISI316L
|
2/4 wires 4-20mA;
Hart Protocol
|
|
|
| Gems Sensors >> Electro-optics Level Switch |
| What is the difference between 'sinking' and 'sourcing?'
|
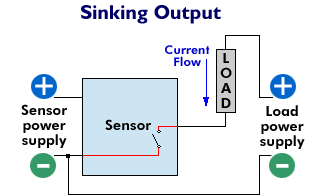 ?? ??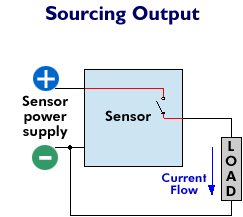
Sinking and sourcing are terms used to describe how an associated load (the device being turned on or off by the sensor) is powered in relation to the sensor. Sinking, the more widely used of the two, involves the switching of load current (power) supplied by a power source external to the sensor. In a sinking configuration, current passes through the load first, through the output switch of the sensor second and lastly to ground. A sensor with a sinking output switches the ground, or negative, leg of the circuit. In contrast, sourcing refers to a configuration in which the sensor is the source of the current required to power the load. In a sourcing situation, current supplied by the sensor passes through the load second and then to ground. A sensor with a sourcing output switches the positive leg of the circuit.
|
|
| Gems Sensors >> Electro-optics Level Switch |
| What is meant by "CMOS/TTL logic?" |
|
TTL stands for Transistor-Transitor Logic and is considered a logic family. A logic family is a collection of different IC chips that have similar input, output and internal circuit characteristics, but that perform different logic functions. CMOS, which stands for Complementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor, is another type of transistor logic family that has become more popular than TTL in recent years thanks to higher speed and lower power consumption (e.g. the 0.5 mA associated with the CLS-1200's 5 VDC output option is sufficient to drive only one TTL logic gate versus ten CMOS gates). The majority of today's large-scale ICs, such as microprocessors, use CMOS.
|
|
| Gems Sensors >> General |
| Is Gems Sensors ISO certified? |
| Yes, Gems has ISO 9001 certification |
|
| Gems Sensors >> Electro-optics Level Switch |
| What is the difference between Wet Sink and Dry Sink? |
| Wet sink means the load is energized ("ON") as long as the sensor tip is immersed in fluid. Dry sink means the load is energized as long as the sensor tip is dry (i.e. not immersed in fluid).
|
|
| Barksdale >> Pressure Switch |
| Is there a repair kit for the explosion proof bourdon pressure switch used in the oil patch market? |
| Yes. Barksdale offers repair kits, B1S-S48SS-L5 or B1S-S48SS, for the non-UL B1X-S48SS models used in the oil patch market. Barksdale does not offer repair kits for our standard explosion UL approved bourdon tube switches.
|
|
| Barksdale >> Pressure Switch |
| Where can I find a listing of UL approvals for Barksdale pressure switches? |
| Click here to view a listing of UL approved Barksdale pressure switches. |
|
|
|

